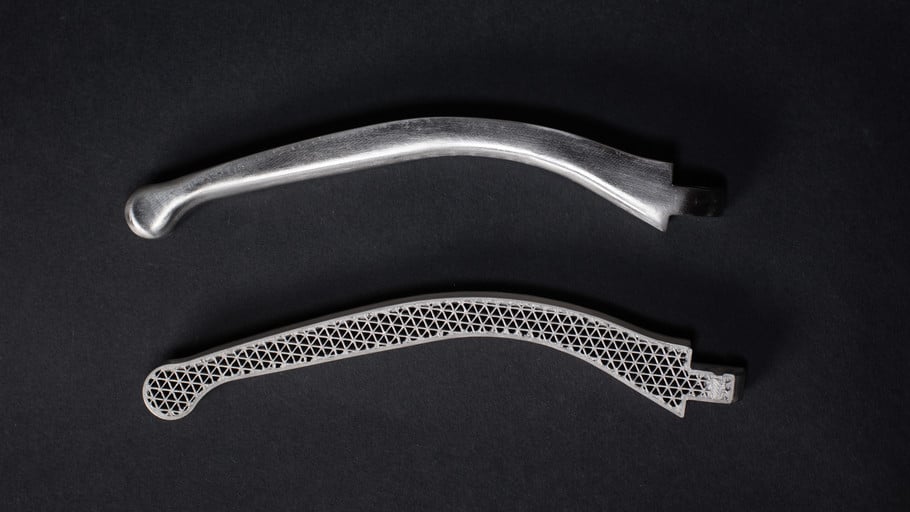
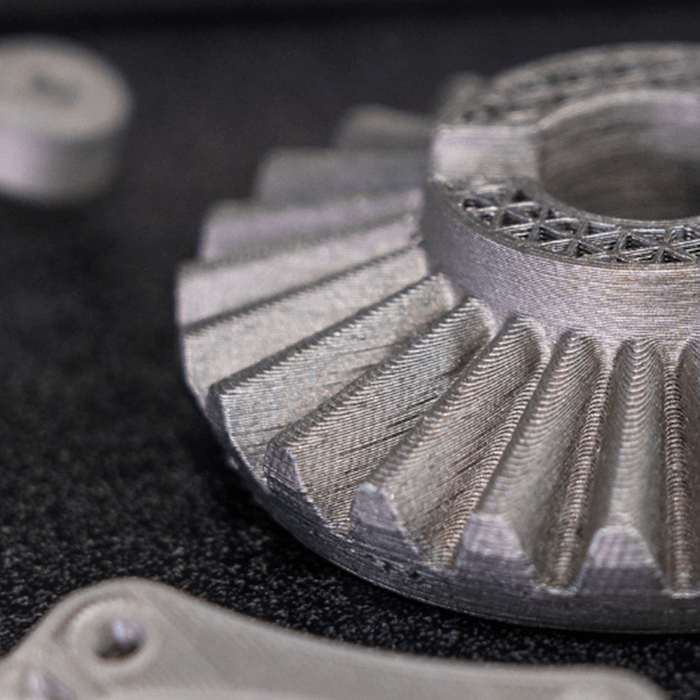
3D Printed Tooling: Explore the Possibilities of Metal FFF
As a technology that has opened up new possibilities for creating complex and customized parts, 3D printing has the potential to transform the world of manufacturing. One of the most exciting developments in this field is the use of Fused Filament Fabrication (FFF), particularly metal FFF, to create 3D printed
3D Printed Tooling: Explore the Possibilities of Metal FFF Read More »